A biconvex lens is suitable for situations where one conjugate distance is 0.2 to 5 times the other conjugate distance. The performance of this lens shape is suitable for situations where the object distance and image distance are the same.
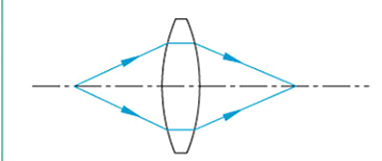
There is also an external lens in the biconvex lens, which has a smaller spherical aberration.
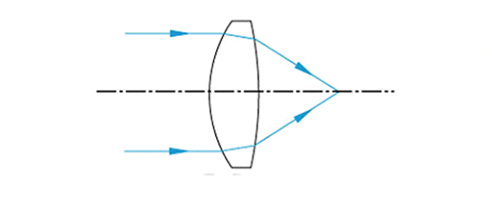
Appearance lens:
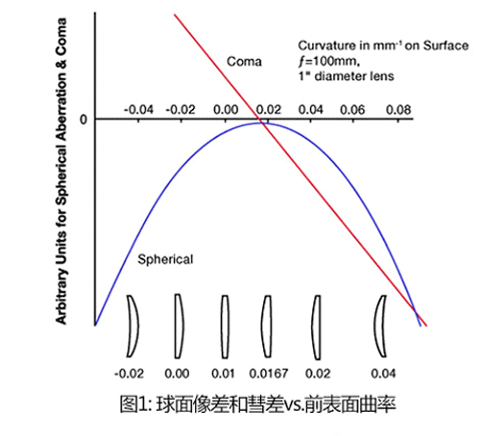
The external lens design is used to minimize spherical aberration and coma (aberrations introduced by light that is not on the optical axis), while still utilizing the spherical surface to form the lens. Using spherical design makes the outer lens easier to manufacture than non spherical lenses, reducing costs. Each side of the external lens is polished to have different curvature radii, providing better performance for spherical single lenses. For small diameter input beams, the external lens even has diffraction performance. These lenses are typically used in high-power applications where achromatic adhesive lenses cannot be used. The design of the external lens is to minimize aberrations while still utilizing a spherical surface to form the lens. These lenses are optimized for infinite conjugate ratios and are highly suitable for focusing collimated beams or collimating point light sources.
| Outer diameter | 9.00 |
|---|---|
| coating film | A:BBAR Ravg < 1% |
| material | H-K9L(Schott BK7) |
| design wavelength | 632.8nm |
| Focal length tolerance | ±1% |
| Profile Tolerance | +0.0/-0.1mm |
| Tolerance | ±0.1mm |
| Facial shape | λ/4@632.8nm |
| finish | 60/40 |
| eccentric | <3arc min |
| Effective aperture | >90% |
| Chamfer | <0.2×45° |
| effective focal length | 12.00 |
| Curvature radius | 11.72 |
| back focal length | 10.75 |
| Center Thickness | 3.60 |
| Edge thickness | 1.80 |






![62569af7bd93a1[1]](https://asphericoptics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/62569af7bd93a11.jpg)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.