Choose an achromatic lens:
Achromatic lenses are a good choice for any demanding optical application because they have substantially better performance than spherical single lenses. Achromatic double bonded lenses are sufficient for most applications with infinite conjugation, and double bonded lenses are an ideal choice for finite conjugation.
However, the adhesive used in these optical components reduces their damage threshold and limits their usability in high-power systems. Dual lens with air separation is an ideal choice for high-power applications because their damage threshold is greater than that of achromatic laminated lenses. In addition, double laminated lenses with air gaps have two more design variables than double laminated lenses, as the inner surface of the lens does not need to have the same curvature. These additional variables are due to the fact that the air gap dual lens outperforms the double bonded lens in terms of transmission wavefront error, spot size, and aberration. However, spatially spaced doublet lenses are also more expensive than double laminated lenses.
Achromatic triple lenses can be designed for both finite and infinite conjugate ratios. These triple lenses have a low refractive index optical element in the middle, which is glued between two identical high refractive index external optical elements. They can correct axial and lateral chromatic aberration, and their symmetrical design has better performance than laminated lenses.
Double laminated lens:
Achromatic dual lens has more advantages than simple single lens. They include color difference reduction, improved off-axis performance, and smaller focal spot size. These doublet lenses have a positive focal length and are optimized for wireless conjugation ratio.
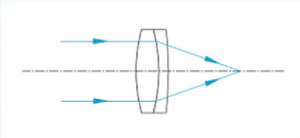
Air gap dual lens:
Air gap dual lens has better performance than double laminated lens because their lenses are separated. These optical components are ideal choices for high-power applications because their damage threshold is higher than that of double laminated lenses. These doublet lenses have a positive focal length and are optimized for infinite conjugate ratios.
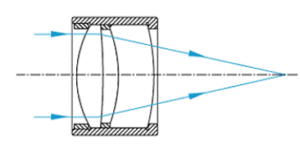
Double lens pairs:
Achromatic dual lens pairs have the advantages of achromatic lenses and are optimized for finite conjugate ratios. These lenses are an ideal choice for image relay and magnification systems.
Achromatic triple lens:
Achromatic triple lens has better performance than achromatic double lens. A chromatic aberration correcting triple lens is a simple lens that can correct all major chromatic aberration. Steinheil triple lenses are optimized for finite conjugate ratios, while Hasting triple lenses are optimized for infinite conjugate ratios.
| Outer diameter | 6.00 |
|---|---|
| coating film | A:BBAR Ravg < 1% |
| design wavelength | 632.8nm |
| Focal length tolerance | ±1% |
| Profile Tolerance | +0.0/-0.1mm |
| Tolerance | ±0.1mm |
| Facial shape | λ/4@632.8nm |
| finish | 60/40 |
| eccentric | <3arc min |
| Effective aperture | >90% |
| Chamfer | <0.2×45° |
| effective focal length | 10.010 |
| Curvature radius R1 (mm) | 6.546 |
| Curvature radius R2=R3 (mm) | -4.055 |
| Curvature radius R4 (mm) | -23.230 |
| Back focal length BFL (mm) | 7.555 |
| Center thickness Tc1 (mm) | 3.60 |
| Center thickness Tc2 (mm) | 0.80 |
| Material Lens1 | SK9 |
| Material Lens2 | SF15 |






![62569bdec981c[1]](https://asphericoptics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/62569bdec981c1.jpg)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.